PCI express
The choice of processor also determines how extensible a system is. The main extension mechanism in modern systems is the PCI express (PCIe) bus. This is a serial bus that connects additional devices to the main system.
Each processor provides a fixed number of PCIe lanes, which are duplex serial connections. Each device connected to the PCIe bus requires a number of PCIe lanes to take advantage of its bandwidth.
There have been multiple version of PCIe is the past years, each increasing the maximum available transfer rate per lane significantly. Each generation has effectively doubled the available bandwidth.
The table below shows that that the bandwidth for a single lane between generation 3 and generation 4 has jumped from 1GB/s to 2GB/s.
Device |
PCIe Connection |
Max. Transfer Rate |
|---|---|---|
Graphics Card |
x16 Gen 3 |
16GB/s |
Graphics Card |
x16 Gen 4 |
32GB/s |
NVMe SSD |
x4 Gen3 |
4GB/s |
NVMe SSD |
x4 Gen4 |
8GB/s |
Infiniband HCA |
x16 Gen3 |
16GB/s |
Infiniband HCA |
x16 Gen4 |
32GB/s |
Graphics cards and Infiniband network cards typically require a x16 connection. That means, they will occupy 16 PCIexpress lanes each.
Modern NVMe solid state drives are also connected to the PCIe bus and require a x4 connection, so they occupy 4 lanes.
It is possible for devices to share PCIe lanes, but this decreases the effective bandwidth and increases the latency of each transfer.
When designing a system, keep in mind the total number of available PCIe lanes and then gradually add devices. E.g. if a CPU has 48 PCIe lanes, that means it can only host up to three x16 CPUs. If the system also contains a NVMe SSD or an Infiniband network card, the amount of support GPUs per CPU decreases.
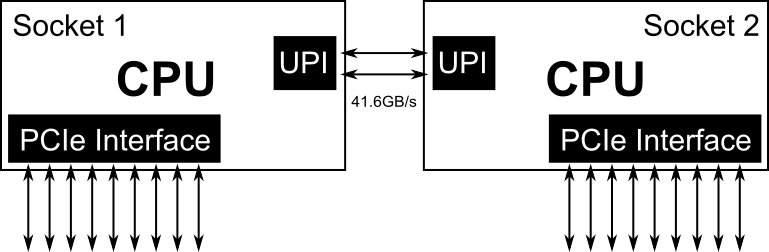
While you can add more PCIe landes by adding more than one processor, keep in mind that if two devices that are connected with different processors and need to communicate with each other, their effective bandwidth will be limited by the inter-socket connection
Connectors
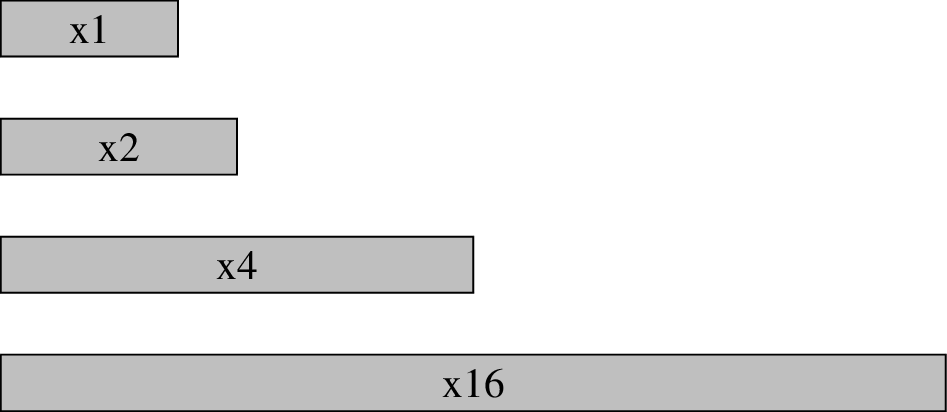
When looking at PCIe cards, you can easily determine the amount of lanes they need based on their connector.
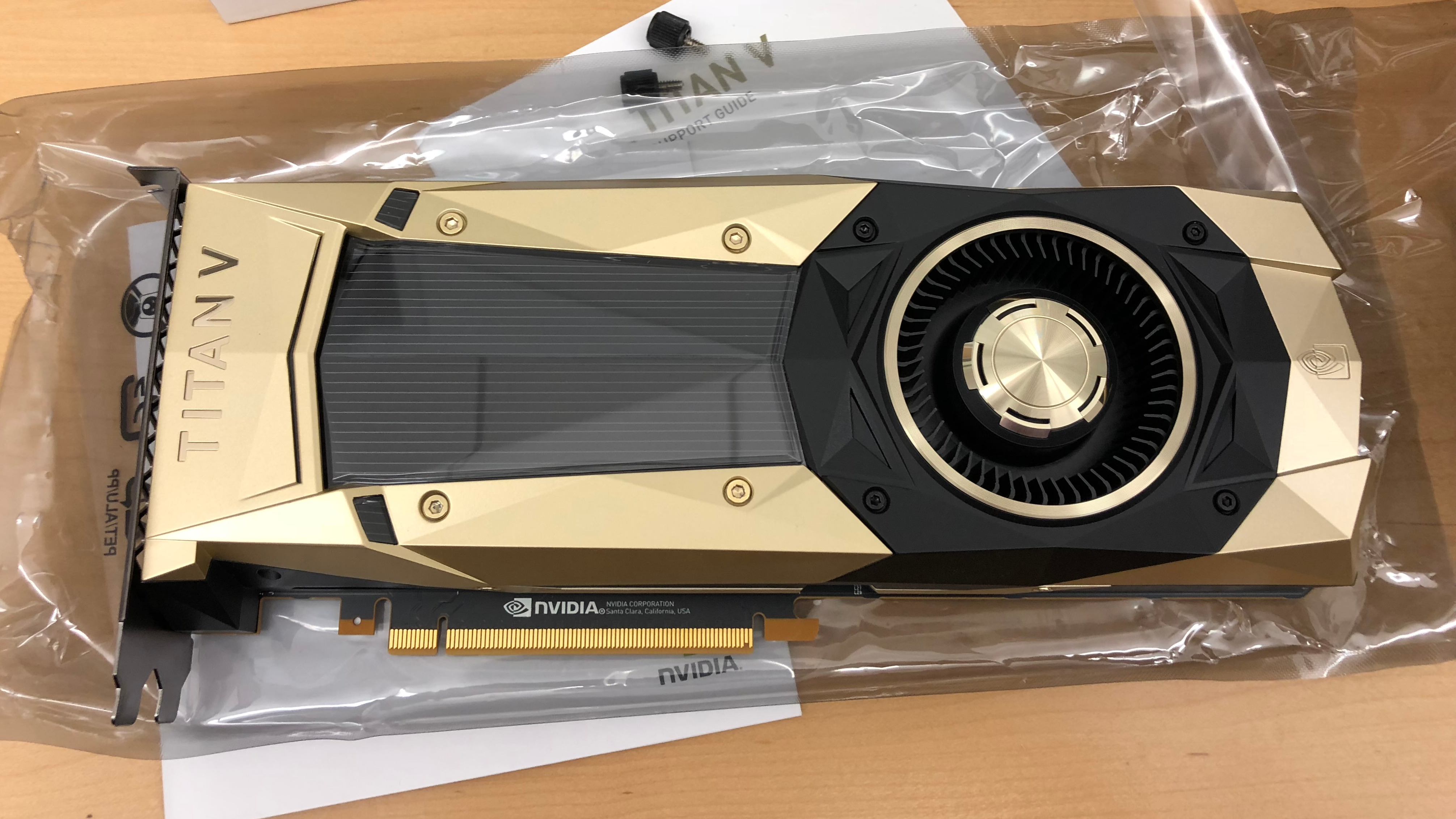

NVIDIA TITAN V PCIe card with x16 connector
If you connect a card with a small connector in a larger slot, it will still work.
Make sure you are aware of the amount of space you have in your server enclosure, since PCIe cards come in different sizes. There is full-length, half-lenght, and full height and half height cards.
In some system PCIe risers are needed. These allow PCIe cards to be installed away from the system board to preserve space.
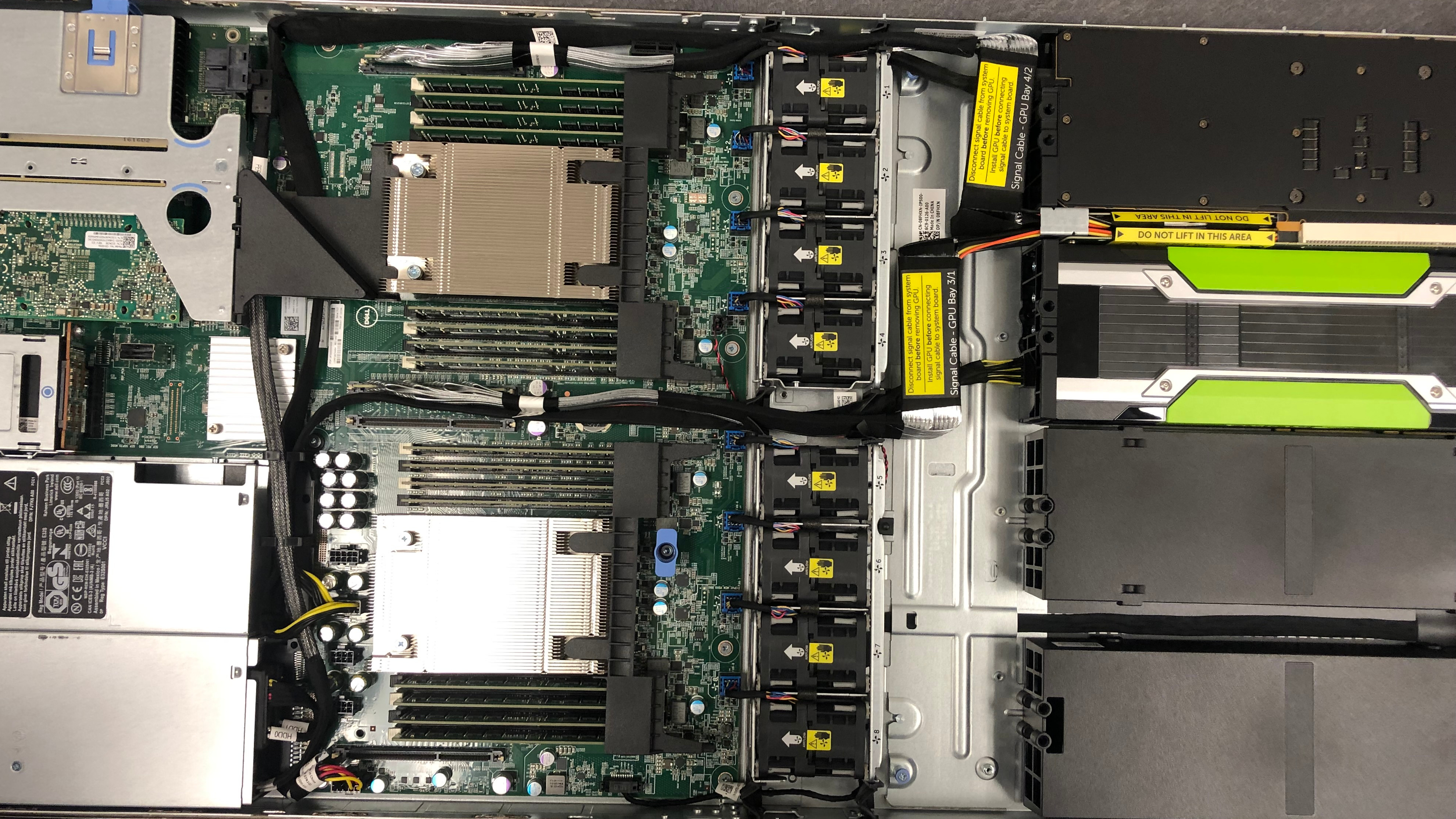
Example of a GPU system with PCIe riser cables: The GPUs are flat parallel to the system board in front of the system. A PCIe riser cable is used to connect the cards to the system board.